How to Read a Nonprofit Balance Sheet
How to Read a Balance Sheet?
Reading a balance sail is of import in determining the fiscal wellness of a visitor. The balance sheet, also known as the statement of financial position, is one of the three primal financial statements. Information technology summarizes a visitor's fiscal position at a point in time. The balance sheet is unlike the other primal financial statements that represent the flow of money through various accounts beyond a period of time.
The balance sheet is frequently considered the most important of the three statements, every bit information technology tin exist used to determine the health and durability of a business. For case, when doing credit analysis , a lender studies the strength of the remainder canvas earlier determining if the cash flows are plenty to service the debt. Hence, there is a constant focus on maintaining a strong and healthy balance sheet.
The next sections describe the construction of the balance canvas and how to read different parts of the balance sheet. They also discuss the important relationships between the other statements and the residual sheet, too every bit how to read the notes.
Structure of the Balance Sail
The balance sheet has four major sections – Assets, Liabilities, Shareholder'south Equity , and Notes. Each of the first three sections contains the balances of the various accounts under each heading. The notes department contains detailed qualitative information and assumptions made during the preparation of the residuum sail.
More than details near the structure of the rest sheet and its relationship to the other financial statements can be found in the gratuitous CFI course on Reading Fiscal Statements.
1. Assets
The assets section of the balance sheet contains the asset accounts of the concern. They are accounts that lead to the generation of hereafter greenbacks inflows similar accounts receivable or are used in the business similar property, plant, and equipment (PP&Due east). The section is further subdivided into 2 parts – Current Assets and Non-Current Assets.
Electric current Assets : These are assets with an bookkeeping life of less than ane year. They include accounts like accounts receivable, inventory, cash and cash equivalents, and advances. The current avails form the basis of the working uppercase of the company. The current assets department is often reviewed in conjunction with the current liabilities section of the balance canvass.
While reading the electric current assets section of the balance sheet, it is of import to check for nugget overstatement, such as large accounts receivable due to an improper allowance for doubtful accounts. Farther quality of assets cannot be straight adamant using the balance canvass alone.
Continuing with the accounts receivable example, the quality of receivables tin often be found in the notes to the remainder sheet, which breaks down the receivables by age and credit quality. Older receivables are likely to turn into bad debts.
The following metrics can be used to clarify the current assets of a visitor:
- Days Sales Outstanding
- Cash Ratio
- Electric current Ratio
Non-Current Assets: These are assets with a useful life of more than one twelvemonth. They include accounts like the belongings, constitute equipment, state, goodwill. They are the company'southward avails that are used to generate revenues and drive the primary business organisation activity. Information technology is important to read the non-electric current assets section in relation to the notes and the income argument.
For example, the section includes property, plant, and equipment, which must be read in conjunction with notes nigh the depreciation policy. The notes to the balance sheet, as well as the cash menses statement, besides detail the changes in fixed assets like PP&Eastward. The changes are not clearly reflected in the remainder sheet. The notes may too item the breakdown of assets in the PP&E account and their useful lives.
Goodwill is often a large portion of the total assets of a firm. It is an intangible asset that arises primarily from acquisitions. Goodwill is checked for impairment every yr and is written-off when it is no longer valuable. Details almost the value of goodwill and its components are listed in the notes to the balance sheet. Since goodwill impairment is a value judgment, it is important to read the goodwill with notes department of the balance canvas.
The following metrics tin be used to analyze non-current assets:
- Asset Turnover Ratio
- Uppercase Expenditure Ratio
2. Liabilities
The liabilities section of the balance sheet contains the liability accounts of the business. These are the obligations of the business to exterior parties that arise from usual concern operations and financing activities. This section is besides divided into two subsections – Current Liabilities and Non-Current Liabilities.
Current Liabilities: These are liabilities that are due in less than a yr. The current liabilities section contains accounts like accounts payable, unearned income, electric current portion of long-term debt. The section is read in conjunction with the current assets section of the residue sheet.
Current liabilities form the other terminate of the working capital of the business. They are the obligations that must exist met using the greenbacks flows from the current avails and other funding sources. While reading the rest canvas, it is of import to report the company'south brusk-term obligations to check for any liquidity bug that may ascend in the near term.
The following metrics can be used to analyze the current liabilities of a company:
- Days Payable Outstanding
- Quick Ratio
Not-Electric current Liabilities: These are liabilities with an bookkeeping life of more than one yr. Typically, the non-electric current liabilities section includes items such as long-term debt, lease obligations. The section is important, as information technology forms one part of a visitor's capital letter structure and is essential in major analyses, such as valuation and credit analysis.
The section's well-nigh important part is long-term debt. The long-term debt number on the residue sheet is an aggregate number, which pools all the debt issued by the company. The details of the figure are found in the notes section, which breaks downwards the debt by issuance. The annotation provides important details similar maturity, interest rate, and other terms of debt. The information is essential to evaluate the majuscule construction and perform credit analysis if new debt needs to be issued.
Following metrics can be used to analyze not-current liabilities:
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio
- Debt-to-Capital letter Ratio
3. Shareholder'due south Equity
The terminal major section of the balance canvas is shareholder's equity. This department summarizes the value that accrues to the equity holders in the concern. It includes accounts such as paid-upwards capital via unlike classes of stock similar common stock and preferred stock, retained earnings, accumulated other comprehensive income, contributed surplus, etc.
The shareholder'due south equity section is essential from the point of view of valuation. Often, financial statements volition include a divide statement detailing the changes in shareholder disinterestedness. The paid-up upper-case letter is usually the largest item here. Information technology is the amount raised from equity holders past issuing shares in the business.
The other items of importance are retained earnings and other comprehensive income. Retained earnings are the portion of the internet income retained in the business for time to come employ after the distribution of dividends. Some other comprehensive income is the income generated from a source non directly related to the chief business activeness. A typical example of such income is the income generated from hedging activities and other fiscal instruments.
Other comprehensive income is not the well-nigh transparent effigy. It is important to dig deeper into the effigy too. Many of the financial instruments that contribute to other income are not listed on the balance canvas. They are instead described in the notes. It is important to understand the details of such fiscal exposures, as many of the instruments are complex, and the balance sheet number is often based on modeling assumptions.
The price-to-book ratio is a metric that can exist used to analyze the shareholders' equity section.
Case Study: Western Product Forests (WEF)
The following is an case of analyzing a existent-world balance sheet. The data comes from the fiscal statements of Western Forest Products (WEF), a lumber company based out of British Columbia, Canada. The analysis that follows goes over the of import accounts on the balance sheet and presents a quantitative analysis that can help measure the quality of the balance sail in a mode that makes it comparable to the balance sheets of other companies.
Some of the relevant accounts for Western Forest Products are discussed below.
Inventory
WEF is in the business organisation of selling lumber, which means that almost of its revenues are driven by the value of the lumber they sell. Hence it is of import to read the details of how they carry their inventory. Co-ordinate to the balance canvas notes, the inventory is carried at the lower of price and net realizable value (NRV) .
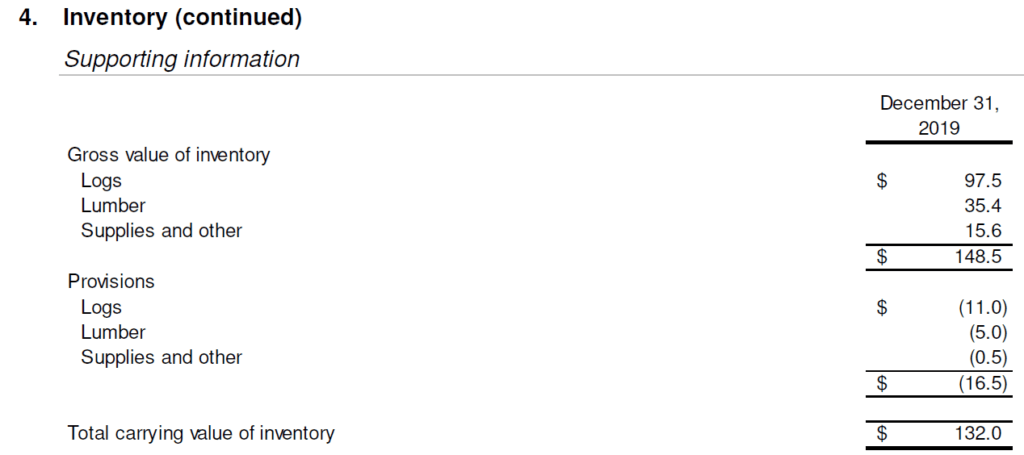
Since timber is an actively traded commodity, information technology comes with an observable price that can exist used to value the inventory. The above data also highlights one of the major risks of the business organisation that the revenue is sensitive to market movements. The notes likewise requite the breakup of the inventory equally illustrated in the tabular array below:
Trade Receivables
Receivables form an important part of WEF's balance sheet, as they stand for sources of cash menstruum. The greenbacks flow is necessary to meet the company's curt-term obligations. Though the residual sheet does non include an exclusive note for receivables, the note regarding financial instruments gives a breakdown of receivables by historic period. Based on the note, merely about 3.v% of receivables in 2019 were late, which indicates the high quality of receivables.

Biological Avails
The biological assets section is the most unique item in the rest sheet of WEF. Biological assets are the woods state owned by the company for timber production. The asset is carried at off-white value on the remainder canvas, which ways that number is subjective. It is important, and its valuation details are covered in the notes. The details can exist a useful guide to revaluing the assets during analysis.
Debt
WEF carries a long-term debt of about $114 million on its books. The nature of the long-term debt is again fabricated clear in the notes. Co-ordinate to the notes, the company drew from a $250 million credit facility.
Furthermore, the interest charge per unit on the debt is 5.45%, which is college than the iv.56% rate in the previous year. It indicates increased credit gamble in the business, which is clearly evident from the increased debt-to-upper-case letter ratio.
Quantitative Analysis
A detailed reading of the residual sail is incomplete without quantitative assay. Ratio assay of the residue sheet is a good first footstep in determining the health of the underlying business concern. Ratio analysis tin can and then be augmented with more complex analyses similar the Altman Z-Score . The analysis goes over diverse sections of WEF's balance sheet and performs suitable analyses.
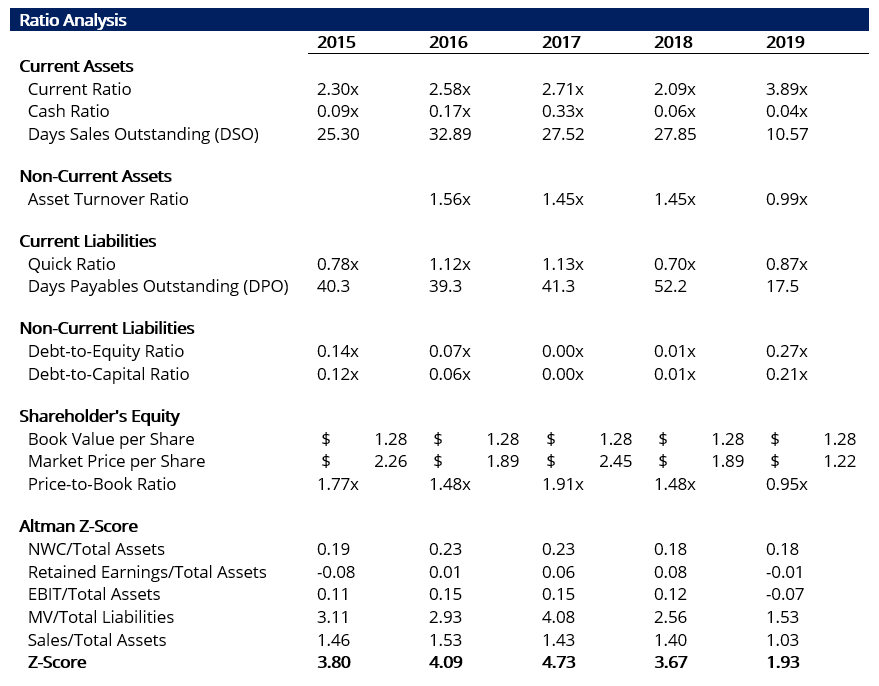
According to the analysis, there was a deterioration in business concern performance in 2019. It is reflected by changes in the following list of ratios:
- The quick ratio declined from i.13x in 2017 to 0.87x in 2019, which indicates liquidity stress. Typically, a good quick ratio is at to the lowest degree i.0x. Too, notation the electric current ratio is much stronger and is indicative of a expert liquidity position. Hence information technology is important to apply multiple ratios to analyze the same variable.
- Debt-to-Upper-case letter: The share of debt increased from less than 1% to 20%. The debt is not related to investment but to come across the business's funding requirements, indicating weak revenue and profits.
- Greenbacks Ratio: There is as well a precipitous decline in the greenbacks ratio from 0.33x to a mere 0.04x. It implies that the company might run across issues in meeting its short-term obligations.
Finally, the Altman Z-Score can exist used as a summary effigy for the quality of the balance sheet. In 2019, it cruel to 1.93 from a health score of iii.67. The figure indicates the company is deadline bankrupt and is clearly a distressed business, according to the Z-Score assay. The following tabular array summarizes the results of the analysis:
More than Resources
To keep learning and developing your knowledge base, delight explore the additional relevant resources below:
- Analysis of Financial Statements
- Financial Argument Notes
- Projecting Residual Sheet Line Items
- Quantitative Analysis
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/finance/how-to-read-a-balance-sheet/
0 Response to "How to Read a Nonprofit Balance Sheet"
Post a Comment